Drone technology is growing as fast as it is being adopted in various economies. From being used just for aerial video and photo shoots, drones have been adopted for fishing, there are underwater drones and drones in agriculture.
Agriculture drones are used to conduct aerial operations that were previously carried out by small aircraft. Drones in agriculture are used for scouting, irrigation, security, spraying insecticides, and recording data for future analysis.
However, unlike when using an aircraft, using drones is more cost-effective and more efficient.
Importance of using drones in agriculture
Farmers are shifting to the use of drones in agriculture due to the advantages that come with them.
The following are some of the benefits of using drones for farming;
Better data collection
Before the adoption of drone technology in agriculture, farmers would use satellite images to gather data on their farms. However, the images could not give you a close look into the farm due to the heights of the satellites.
With the introduction of drones in farming, the pilot can fly a drone as close as he would like to the crops. This helps you gather more accurate information about the crops.
This data can also be stored and used to identify patterns.
Increased crop yields
With more accurate data collection using drones in agriculture, you are guaranteed an increase in crop production.
You are likely to identify irregularities in the color of the leaves using photos taken by drones for farming in a certain area. From there, you can take the necessary measures to control crop health problems.
Other field operations taken by a drone to increase crop production include identifying irregularities in soil distribution. This may have an impact on irrigation and knowing where fertility lacks.
Reduces operation cost
Using drones in agriculture significantly reduces the cost of operation compared to using an aircraft.
When using an aircraft, say for hire, you will have to pay for it and pay the pilot as well. A drone on the other hand needs just the drone pilot.
Operations such as irrigation and the application of insecticides may force the farmer to dig deep in their pockets if they are to use an aircraft or other alternatives from a drone.
Easy to use
Drones made for farmers are not as complicated as the ones made for professional photography drones.
This is because the manufacturers know that farmers may not be equipped with high skills to operate drones.
Farming drones have features whereby you can map the route which the drone will follow. You can also set the altitude you want the drone to fly at and just release the drone into the air.
The agricultural drone will simply follow the instructions and collect data for you while conducting other farm activities.
Reduced Co2 emissions
An agricultural drone uses rechargeable batteries for power. This is very different from flying an aircraft that uses fuel to operate.
The use of fuel in aircraft results in more Co2 being released into the air. This could later impact climate change and thus affect crop production.
Saves time
One of the problems that technology is good at solving is losing time and drones for farming are no exception.
When you have a large portion of land, it might take a lot of time to move from one end to the other. However, if you have a drone, you can easily fly it over the crops to inspect a specific area on your land.
Another instance would be when using manual labor to apply insecticide on a piece of land. It will take more time for a single person to spray the crops than a single drone would.
Improves security
Cameras are widely relied on for security purposes. An agriculture drone, being a camera can help keep an eye on your farm.
Intruders will be quickly identified using a drone and the necessary action will be taken. This helps keep your property safe and get the most from your efforts on your farm.
How to choose a drone for agriculture
When shopping for the best agriculture drones, there are several points you need to keep in mind;
Payload capacity
The payload in drone technology refers to the amount of weight the drone can lift. This will include anything attached to the drone such as extra cameras, sensors, spraying liquid, or seeds.
The payload of a farming drone is indicated in the specifications; the higher the payload, the more goods a drone can lift. This translates to fewer trips to reload more goods thus less time will be used.
Battery life
Battery life in a drone will equal the amount of time the drone will stay in the air before asking for a recharge.
While most drones for agriculture have approximately the same battery capacity, there are some factors that affect flight time.
These will include the payload, weather conditions, and the flight mode used.
Signal range
Drones for agriculture vary in the signal range in which the drone connects to the controller.
When you fly a drone out of range, it loses the WI-FI connection to its controller. This means your drone may get lost. To avoid such cases, it is advisable to keep the drone within the line of sight.
Most drones used for farming have a transmission range that can cover up to 120 acres of land. This signal range may remain strong in fields where there are no obstacles such as buildings making it very efficient for farming professionals.
Safety features
Sometimes the drone may get out of range and you risk losing it as we stated earlier. However, with advanced safety features such as GPS tracking, you may recover it with no problem.
Other drone technology features included in some agriculture drones include obstacle avoidance. The obstacle avoidance feature uses sensors on the drone to avoid collision with objects along the flight route.
This feature has proven to be helpful to agriculture specialists who are not well-skilled in flying a drone.
Types of drones used in agriculture
Most agriculture drones fall under rotary or fixed-wing drone categories.
Rotary agriculture drones have one or more propellers while fixed-wing drones have only one propeller at the back.
Each drone type has its advantages and disadvantages as well. Let’s go through them;
- Single rotor drone

A single-rotor farming drone takes the shape of a helicopter and works like one. It consists of one rotor on the upper side of the drone and another one at the tail for controlling the direction.
Single-rotor drones have a fair flight time due to fewer rotors but can carry heavy goods since they have long blades.
- Multi-rotor drones

Multi-rotor drones are widely used in agriculture. This is all credit to their precision.
Multi-rotor drones can take off vertically from any point and can easily move in any direction.
Precision is key in farming when conducting activities such as taking photos or dropping seeds.
The most common multi-rotor agriculture drone is a quadcopter.
- Fixed wing drones
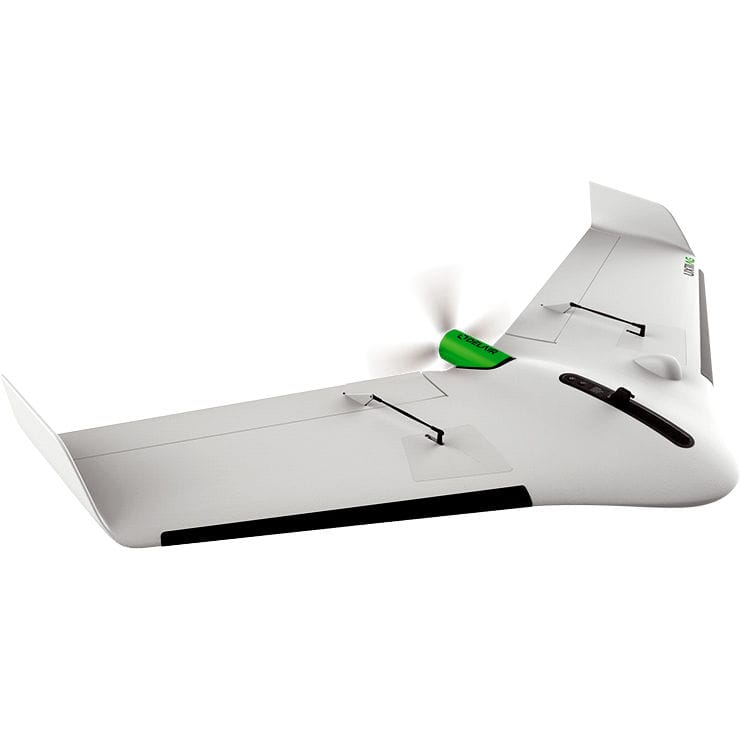

Fixed-wing drones are shaped like an airplane and have a single rotor at the tail end. This propeller gives the drone the thrust required to keep it aloft.
Since there is only one propeller, a fixed-wing drone has a longer battery life compared to other types.
However, unlike a multi-rotor drone, a fixed-wing drone cannot take vertical takeoff or landing. This means it will require a space to use as a runway. This problem is however solved by a hybrid version that combines the advantages of a multi-rotor drone with those of a fixed-wing drone.
What is the future of drones in agriculture
The use of drone technology in agriculture is inevitable. Farmers who use drones can testify to improved production at a lower cost.
The data collected using drone technology will be used to avoid the occurrence of similar outbreaks in the future as well as improve soil conditions on the land.
Drone technology is working towards the development of a mechanical pollinator. This will further help in crop production in the coming days.
Check out this video by Maryland Farm & Harvest for more information on agriculture drones;